November 29, 2012
Parliament Betrays People in Developing Countries Needing Medicines – Bill C-398 Voted Down
Statement from the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network and the Grandmothers Advocacy Network. (link)
NOVEMBER 28, 2012 – We are profoundly disappointed that Parliament has decided to reject reason and overwhelming evidence by defeating Bill C-398, which would have ensured greater access to affordable medicines for people dying of treatable diseases such as AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis in developing countries. By choosing to believe the blatant lies and misinformation circulating about this bill, MPs who voted against the bill have reneged on Parliament’s earlier pledge and have betrayed people in developing countries — including hundreds of thousands of children — who need medicines to prevent suffering and death, including from AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria.
Bill C-398 would have streamlined Canada’s Access to Medicines Regime (CAMR) by cutting red tape that is wholly unnecessary and proven fatal to the future use of the system. The bill would have made it easier for both developing countries and generic drug manufacturers supplying medicines to use CAMR to help save lives and reduce suffering. A previous iteration of the bill (Bill C-393) was overwhelmingly passed in the House of Commons in the last Parliament — before it died in the Senate with the election call. That bill enjoyed support from members of all parties in the House of Commons, reaffirming that this should be a non-partisan issue. Bill C-398 had the support of medical and legal experts, humanitarian activists, faith leaders, AIDS and international development organizations across the country and health activists around the world. Dozens of prominent Canadians supported the call to action, and 80% of the public supports fixing CAMR according to a national opinion poll.
Bill C-398 reintroduced to the House of Commons the same amendments that very strong majority had already previously endorsed. It was a second chance to finish the job of fixing CAMR and supporting developing countries with needed, lower-cost medicines.
It is a travesty that the Harper Government, having made much of its initiative on maternal and child health, would now turn its back on an opportunity to help people dying of treatable diseases — through a smart policy that that would have cost no taxpayer money and, in fact, would make Canada’s frozen foreign aid dollars even more effective, by harnessing the power of generic competition to get less expensive medicines to developing countries. A government that preaches the virtues of markets and “value for money” chose to disregard both; instead, it prioritized its incorrect reading of World Trade Organization (WTO) rules on protecting patents over a workable mechanism for supplying more affordable, life-saving medicines to developing countries struggling with the ravages of the AIDS pandemic and other public health burdens. This is shamefully callous and a discriminatory double-standard for which those who can least afford it pay the ultimate price.
We wish to thank the many champions of this bill, from all political parties, who took Bill C-398 through the legislative process. The fight is not over. Too much is at stake.
But the bottom line is this: after more than eight years of waiting for Canada to deliver on its pledge to help get more affordable medicines to Africa and other developing countries, the world will still have to wait — and people will die preventable deaths because too many Parliamentarians did not have the courage to do the right thing.
For more information please contact:
Richard Elliott
Executive Director
Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network
For more information: www.medicinesforall.ca
About the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network
The Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network (www.aidslaw.ca) promotes the human rights of people living with and vulnerable to HIV/AIDS, in Canada and internationally, through research and analysis, advocacy and litigation, public education and community mobilization. The Legal Network is Canada’s leading advocacy organization working on the legal and human rights issues raised by HIV/AIDS.
About the Grandmothers Advocacy Network
The Grandmothers Advocacy Network (GRAN) is composed of volunteer grandmothers and grand-others from across Canada (http://grandmothersadvocacy.org). We act as a Canadian voice for Africa’s sub-Saharan grandmothers who are caring for millions of children made vulnerable by AIDS. We work for changes in Canadian policies to improve their quality of life.
November 29, 2012
Tentacles coming from your bathtub.
This would look lovely in any self respecting invertebrate friendly bathroom.
Available here. Via Stacy Thinx.
November 29, 2012
Birds on Twitter (this is so seriously awesome)

“Latvian conceptual artist and creative director Voldemars Dudums created this insanely clever bird feeder using an old computer keyboard and some cubes of bacon fat. When the birds would fly down to snack their inadvertent key presses were fed to an api that parsed each little tap into a bonafide tweet on the @hungry_birds Twitter account”
By Voldemars Dudums, text via Colossal.
November 28, 2012
Adding to the “dumb ways to die” list: Because of a patent. #C398
Apologies if you haven’t seen this yet (it will stick to your brain like nothing you’ve ever experienced), but it provides a little light hearted context for a serious issue.
Serious issue explained in a piece entitled A moment of your time: about Bill C-398 and how Canadians can contribute to global health.
(Video campaign by McCann Melbourne, animation by Julian Frost).
November 28, 2012
Best Moon Related YouTube Comment Ever…
Hilarious.

Source Unknown.
November 27, 2012
Extinction typography #beautiful
Check out this album cover for the Finnish band Burning Hearts. Note how the creatures (all extinct) spell out the name of the album, “Extinctions”.
By Emil Bertell and Kea Bertell, via NotCot.org.
November 27, 2012
Conceptual space colony art from the 1970s: Kinda want to live there.
Address: Toroidal Colonies (in the vicinity of Earth’s orbit)
“NASA commissioned much conceptual work focused on moving people to space, both for habitation and travel. The artwork featured here come from three summer studies by NASA Ames, conducted in California during the 70s. They feature beautifully fantastic landscapes inside massive structures… a vision of a utopian life inside an artificial atmosphere.”
From NASA Ames Research Center, via Visual News (text by Benjamin Starr)
November 26, 2012
A moment of your time: about Bill C-398 and how Canadians can contribute to global health
Dear Canadians:
On wednesday, a very important piece of policy will be discussed in parliament. It’s called Bill C-398 and it deserves our attention. It seems that it has been challenging for some to see its merits, and so, I’d like to take moment to clarify what it’s all about. It turns out that it’s not just important – the narrative is compelling as well: it has a rich history of political intrigue; it is a story where viruses factor in prominently; it has a plot that involves armies of angry grandmothers; and above it all, learning about Bill C-398 can literally save lives.
Note, that the below piece is a re-edit of sorts, an update of a piece I wrote for Boing Boing that was an attempt to discuss that political intrigue. And also note that there is some bias in my commentary – but I think this is natural. There are obviously a variety of viewpoints involved and my own happens to disagree with those who choose to listen to corporate and political interests – more so when those interests rely on reasoning that is often spun a certain way to misrepresent useful facts. My bias happens to fall on the side of human dignity: something I think we should all spend a moment to contemplate, and something I think all Canadians would feel is a cause worth fighting for.
– – –

“Access to life-saving medicines is not a luxury, but a human right.”
~Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network
To me, the above statement is one of those things that sound like a no-brainer. Put another way, if I were to ask you whether you thought a person’s income should determine whether they live or die from something like HIV/AIDS, then I think you would see that the answer is nothing but obvious. But here I am, in Canada, writing this post, because there is a very real danger that members of my government think that this isn’t such an easy decision after all – that maybe wealth and business interests do matter when dealing with such ethical choices, and that there is a hierarchy where certain lives are worth more than others.
Let me backtrack a bit, and provide a little context. I’d rather not write a rant, emotional and heart wrenching as this discussion can be – I’d prefer to rely on reason, and not on rhetoric. Yes, rhetoric helps, but reason and validity are much more powerful. I want everybody to understand why this is an important issue, one that deserves coverage, and one that deserves our involvement. More importantly, I want everybody to understand why the right thing to do is obvious.
To start, let me mention the letters and numbers that make up the label, “Bill C-398.” Keep them in your head – at least for a moment. If you’re the sort that prefers hearing at least a quick definition, then this one might work:
“Bill C-398 aims to reform CAMR and make it easier for Canada to export affordable, life-saving, generic medicines to developing countries.”
~Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network
If you’re thinking that this is a Canadian thing, then think again. Other rich countries are watching how Canada will behave. There’s always a few in Europe, and apparently even China is curious. In the U.S., the topic appears to be quenched, but the behaviour of the Canadian government could catalyze dialogue. And if you’re not from a rich country? Well, you might actually have lives that will be affected by it, millions of lives even.
Here’s the problem in a nutshell: the developing world is heavily burdened with a variety of diseases, many of which are causing massive numbers of suffering and deaths.
This is understandably big. It’s a huge global challenge, and there are many reasons for why it exists and why it is difficult to both comprehend and fix. However, the presence of effective medicines is not one of the reasons. There is medicine out there that can help, and there is also a flow (sometimes slow) of discoveries that make these medicines better and more effective. In the case of HIV/AIDS, there are drugs that essentially turn the disease from a death sentence to something that is chronic and manageable. I can’t overstate how significant that piece of information is: it tells us that people do not have to die from HIV/AIDS.
So what’s the issue?
The issue is control without regard for doing the right thing: This is essentially about patents. It’s not that patents are bad, but rather that patents can be bad. As you probably already know, patents are a service provided by government to protect an inventor, such that the inventor has an element of control over how their innovation/product gets used. This is generally a good thing, because ultimately it provides order to a process that would get very chaotic very quickly should the patent not exist. However, sometimes the inventor isn’t the best person to make decisions about control. Sometimes, the inventor doesn’t have the best information to take stock of a situation, or sometimes there might be a moral argument where monetary performance should not take precedent. In other words, sometimes, there are special circumstances where you could say it is reasonable that this control is tweaked.
To illustrate this, here are some hypothetical (and not so hypothetical examples):
1. Your country has experienced a massive storm, perhaps one named after a character in Grease, and it has hit the East coast very very hard. Many folks are still without power and water, but there is technology that would be incredibly useful to mitigate this. However, your resources are already stretched and this technology is too expensive at the scale that is required in such an emergency.
2. Someone has declared war on your country. To defend yourself, you would like to utilize a particular product. Unfortunately, it is under a cost prohibitive patent and therefore out of reach.
3. There are markets where your life saving drug is not being sold because no-one can afford them anyway. However, the drug (which could be a matter of life and death for millions) could be made at a cost (i.e. a generic) that makes it accessible in these markets, but if and only if, the patent over them is adjusted.
Here is my point. In all of the above cases, you would like to live in a civil society where the government can step in and forcibly change the patent, because in every case, there is an element of morality involved. And guess what – governments can do this and they do! It’s called a “compulsory license,” and they exist for this very purpose.
In fact, even the WTO is on board with this idea. They recognize that in some circumstances, such as those pertaining to global health, there needs to be an understanding that using such compulsory licenses is both necessary and an obligation. In fact, if you have a hankering for the legalese that outlines this for patents over essential medicines, you need only look up info on the Doha Declaration.
Canada actually took this to heart with a bill that came into force in 2005. Often referred to as “Canada’s Access to Medicine Regime” (or CAMR), it was an effort to put into action, the principles and details provided by the Doha Declaration. It was a way to try and enact compulsory licenses for the home production of generic drugs so that more accessible drugs could be produced. It was a good gesture.
Unfortunately, this initial attempt was flawed. The process was simply way too complicated, contingent on an army of legal expertise to navigate, which was all the more problematic because many of the actors involved did not have the means or access to do this. Indeed, the bill seems to contain a paradox in it, in that it can be interpreted as logically impossible to use. If you look closely, there’s a “you can’t do B until you do A” and a “you can’t do A until you do B” error in the details (see question 9 in this document for more details).
It was also very inefficient in that when a compulsory license was negotiated, it was always a one time affair, a one order affair, with specific amounts that could not be changed despite possible reassessment of needs, only good for one country, etc, etc, etc. Indeed, in the years that the law has been available, it has pretty much sat idle (I believe there has still only been one successful case where drugs were actually made and delivered, which provided ample evidence to demonstrate that this process was difficult at best). In fact, if someone were to asked me how difficult things are, the best description I could come up with, is that is it “catastrophically high maintenance.”
Which (finally) brings us to “Bill C-398.” This bill is basically “the edit.” Its sole purpose is to address the things that made the previous bill so ineffective, and at its heart it allows a more streamline and efficient way to issue these compulsory licenses so that production of these generics is more feasible.
No brainer right?
“Oh, but it’s not that simple,” they say. “There are many counter arguments,” they say. Only these counter arguments tend to sound like this:
Q: Shouldn’t we focus on other aspects of the problem. Like health infrastructure, or public education for HIV?
A: Hmmm… Let me get this straight. A government can only do one thing at a time? Nevermind the fact that passing this bill doesn’t actually cost the taxpayers anything. If anything, research has suggested that the foreign aid that we do provide will likely have greater bang for its buck.
Or maybe something like this:
Q: Wouldn’t these changes effect the pharmaceutical company’s bottom line, which in turn will effect R&D funding, and drive the home costs of medicine up?
A: The language is pretty clear in that these are generics that can only be sold in certain markets. These markets happen to constitute a very small percentage of pharmaceutical revenues (we’re talking single digits here). Oh yeah, plus you get royalties from doing this anyway. Also, there’s nothing stopping you from making your own generic version, so that you can enter the market yourself. Indeed, all research and current evidence would suggest a possible gain in bottom line. Plus, the R&D argument is totally a red herring. If that were so crucial, it might help if you spent less on PR and the like. Sneaky.
But what kills me, is that even if there is a reasonable and say unforeseen cause for concern, the Bill has a freaking “sunset clause” which is basically something that gives all parties a “we’ll see how it goes, in case it’s not working” escape route.
All to say, that because of this kind of political and big pharma semantics, there is a very real likelihood that the Bill will die (perhaps in the next few days when it is up for a second reading). This would be an interesting commentary on the values of our government, although there is already a rich backdrop to this political story.
You should know that this is a Bill that had a previous incarnation two years ago. It once lived in the country calling itself Bill C393, and it was one of those few Bills passed by the House of Commons where party lines were clearly broken. Unfortunately, during that time, the Conservative Senate stalled their vote to make it law, and they did this because they knew that there was an opportunity to “save face” with their industry interests by avoiding the issue altogether.
This was the frustrating part, and I have to admit, my trust in Canadian politics really took a hit. Here, certain members of Senate, a place that traditionally falls in line with the vote of the House of Commons (because that is, after all, the democratic element of decision making), stalled discussion on this Bill 4 times over 4 days, and in doing so, Bill C-393 got killed by association when a new election was called.
To put this in perspective (and to use internet vernacular), let me just say that this horrific series of events represented a political facepalm of the highest possible order. In fact, we invented a term for it: we called it a #megafacepalm.

And so here we are with another attempt. This is the essence of why you should care about BILL C-398. But what can you do?
Well, for starters, you can lend a hand by speaking out. Retweet this blog post, write about it yourself. You should definitely send an email to Prime Minister Harper and a few of his key Members of Parliament by using this ridiculously easy petition. If you’ve got something meatier to say, how about copy pasting this entire list of emails, and let the Canadian government know how you feel. If you’re not Canadian, do these things anyway, and then make this issue pertinent in your own country. This is an urgent matter, and for Canadians, there is only so much time to advocate. It’s really an amazing chance for Canada to lead the way.
You can also immerse yourself in this cause and get as much information as possible. You can check out organizations such as the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network, which has all sorts of great documents including this informative myth versus fact sheet.
If you’re a university student, you can check out your local UAEM chapter. If you’re a Grandmother, you can hear what Grandmothers Advocacy Network have to say. Better yet, check them all out, or join these groups and volunteer your time.
There is also a twitter campaign in progress. Flood the feed with hashtags like #C398, #fixCAMR, #medicinesforall, #cdnpoli and tweet out your support with phrases like:
“Please vote YES to Bill #C398 on Wed! We need to #fixCAMR and improve #accesstomedicines! #cdnpoli”
“Have you signed the petition in support of #accesstomedicines yet? Go to www.medicinesforall.ca! Let’s #fixCAMR & pass #C398!”
If you think the idea of Bil C-398 above seems reasonable and just, please do whatever you can. Because through it all, you should never ever forget: “Access to life-saving medicines is not a luxury, it is a human right.”
November 25, 2012
Teaching scientific editing – Shrimp Running On A Treadmill With The Benny Hill Theme
Useful when teaching abstract writing (could this wording be any more concise and perfectly descriptive).
Also, it’s a shrimp running on a treadmill with the Benny Hill theme.
November 25, 2012
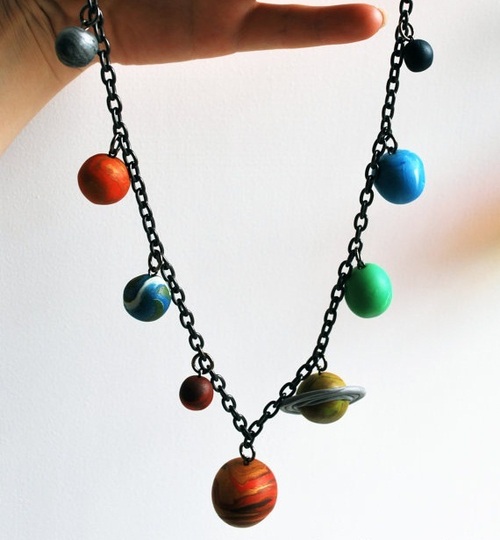
This here: a solar system necklace
Solar System Necklace, Solar System Bracelet, Earth Necklace and Moon Phase Choker by nappyhappy in Swindon, UK (via Stacy Thinx)
November 23, 2012
What was this “Science Dystopia” badge she spoke of?
It was a real treat to have Margaret Atwood out to UBC last night, and she was a delight to host from start to finish.
At the beginning of her talk, she made mention of a science badge – a “Science Scout” badge – and I thought it would interest some folks to share a bit more on her nod to this unconventional thing that came from my lab.
Essentially, a while back, she was kind enough to help design a Science Scout badge.
What is a science scout badge exactly?
Well, it’s one of those things that goes a long while back, and is usually best left unexplained – except to say that searching the internet will get you there.
In a nutshell, the badges are a silly thing, if not amusing, but also a portal into science culture. Usually, these badges are virtual stamps to leave on one’s website, or an opportunity to tell an interesting science story. And on occasion, we do have talented folk who make physical incarnations of them.
In this case, I arranged for one of these talented folk (Rachel Newlin) to make a few of Miss Atwood’s badges. Here is a photo of one of them:
Lovely, isn’t it?
More importantly, I think it’s another great example of science culture. It’s another instance that shows that it’s o.k. for a writer like Margaret Atwood to participate in science things (obviously) – likewise, it’s o.k. for a scientist like myself to participate in storytelling things. It’s really not that strange.
Science isn’t a technical term – it is a form of culture. It’s also a tool or a way to understand and experience the world. And as such, it can be embedded into everything, in large or small parts, technically or philosophically, and we shouldn’t be afraid of it. Perhaps we should be wary of it, but not afraid of it – these are not the same thing. If nothing else, it seems to be a pretty good inspiration for badges.
November 22, 2012
Documentation of blackboard activity: a merging of mathematics and art
“Since 2010, Spanish artist Alejandro Guijarro has been traveling to several Quantum Mechanics institutions across the globe. He photographs their blackboards that are filled with the mathematical scribblings of some of the greatest minds in the world. The photographer walks into each facility’s lecture halls and proceeds to snap shots of the blackboards without modifying the board or interfering with the original arrangement of the space. The ongoing series titled Momentum presents an honest look at the intellectual scrawls, some of which have been wiped away.”
By Alejandro Guijarro. Text by My Modern Met, via Stacy Thinx.
November 22, 2012
Strapping a camera on a pigeon? Sounds about right.
“Photographing with birds is anything but a new idea. It was actually invented a little over a century ago, in 1907, by a German photography pioneer named Julius Neubronner.
Neubronner worked as an apothecary (i.e. an old-school independent pharmacist) and used carrier pigeons to rush deliver medications to clients. After one of his pigeons returned four weeks late, Neubronner came up with the wacky idea of sticking a camera onto his pigeons in order to glimpse into their activities.”
Text by Michael Zhang at Petapixel. There’s also a wikipedia entry on this topic.